Study reveals new insights into immune system role in lung cancer risk
Study reveals new insights into immune system role in lung cancer risk

Study reveals new insights into immune system role in lung cancer risk
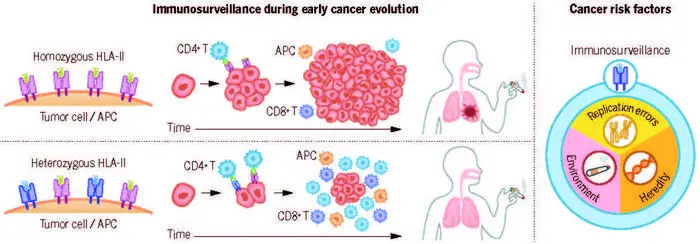
The investigators utilized genetic epidemiology and multimodal genomic analyses of data from the UK Biobank, validating it in FinnGen. Their study focused on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules—the most diverse genes in the human genome and at the core of immune recognition. These genes contain instructions to make proteins, which play a crucial role in presenting foreign antigens on cell surfaces. This process aids the immune system in identifying and eliminating threats such as cancer cells.
Surprisingly, the study found that individuals with heterozygosity (having different versions of a gene) at HLA-II, rather than HLA-I, experienced a decreased risk of lung cancer. This effect was particularly pronounced among smokers, a population already at higher risk for lung cancer due to exposure to carcinogens.