Systemic autoimmune disease in asbestosis rapidly responding to anti-interleukin-1beta antibody canakinumab: a case report
Systemic autoimmune disease in asbestosis rapidly responding to anti-interleukin-1beta antibody canakinumab: a case report
Systemic autoimmune disease in asbestosis rapidly responding to anti-interleukin-1beta antibody canakinumab: a case report - BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders

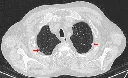
Asbestosis is a progressive interstitial lung disease caused by inhalation of asbestos fibers occurring in subjects with prolonged exposure to asbestos dust.
Clinically, the lung involvement is characterized by the development of bilateral diffuse interstitial fibrosis, more pronounced in the lower lobes, and pleural thickening, leading to shortness of breath and dry cough.
Although not definitively clarified, it is generally accepted that the pathogenesis of pulmonary interstitial inflammation and fibrosis is related to immune mechanisms induced by asbestos .
Among pneumoconioses, silicosis represents the most frequent condition inducing systemic autoimmune disorders . However, also asbestosis is known to be associated with serum antinuclear antibody (ANA), rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity , and may be complicated by autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) .